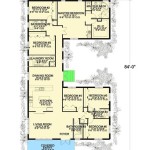
What Is a Floor Plan in Building Construction Terms?
In the realm of building construction, a floor plan serves as a fundamental document, acting as a blueprint for the layout of a structure. It is essentially a scaled diagram viewed from directly above, depicting the arrangement of rooms, walls, doors, windows, and other essential architectural features at a particular level of a building. Understanding the purpose and elements of a floor plan is critical for architects, builders, contractors, interior designers, and even homeowners involved in any construction or renovation project.
A floor plan is more than just a simple sketch; it is a detailed and precise representation of a building's interior, allowing stakeholders to visualize the space and understand the relationships between different areas. It provides critical information needed for construction, including dimensions, material specifications, and the location of structural and mechanical systems. Without a well-developed and accurate floor plan, projects can suffer from delays, errors, increased costs, and potential structural problems.
Floor plans are typically created using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software or Building Information Modeling (BIM) tools, enabling architects and designers to generate highly detailed and accurate drawings. These digital tools allow for easy modification and collaboration between different disciplines involved in the construction process. However, hand-drawn floor plans are still used in some cases, particularly for initial conceptual designs or smaller-scale projects.
The complexity of a floor plan can vary significantly depending on the size and complexity of the building. A simple residential floor plan might only include the basic layout of rooms, while a commercial floor plan could incorporate detailed information about mechanical systems, electrical layouts, and fire safety measures. Regardless of the complexity, the core purpose of a floor plan remains the same: to provide a clear and comprehensive representation of the building's interior for all stakeholders involved in the construction process.
Key Elements of a Floor Plan
A floor plan is comprised of various elements, each providing specific information about the building's layout and construction. Understanding these elements is essential for interpreting and utilizing floor plans effectively.
Walls: Walls are represented as solid lines on a floor plan, indicating the boundaries of rooms and the structural framework of the building. The thickness of the lines may vary to differentiate between load-bearing and non-load-bearing walls. Dimensions are typically included to specify the length and thickness of each wall.
Doors: Doors are shown as arched openings with a line indicating the direction of the door swing. This information is crucial for understanding the flow of movement within the building and ensuring that doors do not obstruct pathways or interfere with furniture placement. The width of the doorway is also typically specified.
Windows: Windows are represented as two or three parallel lines within a wall, indicating the location and size of the window opening. The type of window (e.g., sliding, casement, double-hung) may also be denoted using specific symbols or abbreviations. Window placement is critical for ensuring adequate natural light and ventilation within the building.
Rooms: Each room is clearly defined by its surrounding walls, and the name of the room (e.g., bedroom, living room, kitchen) is typically labeled within the space. The dimensions of each room are also indicated, providing accurate measurements for furniture placement and space planning.
Fixtures and Appliances: Floor plans often include the placement of key fixtures and appliances, such as sinks, toilets, bathtubs, stoves, refrigerators, and washing machines. These are represented by specific symbols and their dimensions are often included to ensure proper fit and functionality.
Stairs: Stairs are shown as a series of steps with an arrow indicating the direction of ascent. The number of steps, the rise and run of each step, and the overall dimensions of the staircase are typically included. Stairwell design is critical for ensuring safe and comfortable access between different levels of the building.
Dimensions: Dimensions are perhaps the most crucial element of a floor plan, providing accurate measurements for all features and spaces. These measurements are typically expressed in feet and inches or in metric units, depending on the conventions used in the region. Dimensions are essential for ensuring that the building is constructed according to the design specifications.
Symbols and Abbreviations: Floor plans often utilize a variety of symbols and abbreviations to represent specific features, materials, and equipment. A legend or key is typically included to explain the meaning of each symbol and abbreviation, ensuring that the floor plan is easily understood by all stakeholders.
The Importance of Floor Plans in Building Construction
Floor plans hold significant importance throughout the entire building construction process, from initial design to final construction and beyond. Their accuracy and clarity can have a direct impact on the success of the project.
Design and Planning: Floor plans are essential for the initial design and planning stages of a building project. They allow architects and designers to explore different layouts, experiment with spatial arrangements, and visualize the overall flow of the building. By analyzing the floor plan, stakeholders can identify potential problems early on and make necessary adjustments before construction begins, saving time and money.
Communication and Collaboration: Floor plans serve as a common language for communication and collaboration among all parties involved in the construction process. Architects, engineers, contractors, subcontractors, and clients can all use the floor plan to understand the design intent and coordinate their respective tasks. This shared understanding helps to minimize misunderstandings and errors, ensuring that the project stays on track.
Permitting and Approvals: Floor plans are typically required for obtaining building permits and approvals from local authorities. These plans demonstrate that the proposed building meets all applicable building codes and regulations, including requirements for safety, accessibility, and environmental protection. Accurate and detailed floor plans are crucial for ensuring that the permitting process goes smoothly and efficiently.
Construction Execution: During the construction phase, the floor plan serves as a guide for builders and contractors. It provides detailed information about the location of walls, doors, windows, and other features, enabling them to accurately construct the building according to the design specifications. The floor plan also helps to coordinate the work of different trades, such as plumbers, electricians, and HVAC contractors, ensuring that all systems are properly installed and integrated.
Cost Estimation: Floor plans are used to estimate the cost of construction materials and labor. By calculating the square footage of the building and identifying the types and quantities of materials needed, contractors can develop accurate cost estimates. This information is essential for budgeting and securing financing for the project.
Marketing and Sales: Floor plans are also used for marketing and sales purposes, allowing potential buyers or renters to visualize the layout of the building and understand the size and arrangement of different spaces. A well-designed floor plan can be a powerful tool for attracting interest and generating sales.
Types of Floor Plans
Floor plans are not monolithic entities; they can be categorized based on purpose, detail level, and presentation style. Understanding these variations helps in selecting the right type of floor plan for a specific task or audience.
Conceptual Floor Plans: These are preliminary sketches or diagrams that explore different design ideas and spatial arrangements. They are typically less detailed than other types of floor plans and are used for brainstorming and initial design development.
Construction Floor Plans: These are highly detailed and accurate floor plans that are used for construction purposes. They include all necessary dimensions, annotations, and specifications needed to build the building according to the design intent. These are often included as part of a larger set of construction documents.
Presentation Floor Plans: These are visually appealing floor plans that are used for marketing and sales purposes. They often include color renderings, furniture layouts, and other details that help to showcase the building's potential. They are designed to be easily understood by a non-technical audience.
Reflected Ceiling Plans: While technically not a floor plan, it is closely related. These plans show the layout of the ceiling, including the location of lights, sprinklers, HVAC vents, and other ceiling-mounted fixtures. They are used by electricians, HVAC contractors, and other trades to install these systems correctly.
Furniture Floor Plans: These plans show the placement of furniture within the building. They are used by interior designers and homeowners to plan the layout of rooms and ensure that furniture fits properly within the available space. These can sometimes be overlaid on a construction floor plan for a comprehensive view.
As-Built Floor Plans: These are floor plans that are created after the building has been constructed. They reflect any changes that were made during the construction process and provide an accurate record of the final building layout. These are important for future renovations or maintenance work.
The selection of the appropriate type of floor plan depends on the specific needs of the project and the intended audience. By understanding the different types of floor plans and their respective purposes, stakeholders can ensure that they are using the right tool for the job.

Floor Plan Wikipedia

How To Read A Floor Plan With Dimensions Houseplans Blog Com

Floor Plan Designing Buildings

15 Key Floor Plan Symbols 74 Architectural Abbreviations Foyr

How To Read A Basic Floor Plan Lofty Building Group

How To Properly Read Floor Plans And What Details Look For

Sample Floor Plan Image With The Specification Of Diffe Room Sizes Scientific Diagram

How To Read Construction Plans Like A Pro

12 Examples Of Floor Plans With Dimensions

How To Read A Floor Plan With Dimensions Houseplans Blog Com
Related Posts