What Is a Floor Plan in Building Construction?
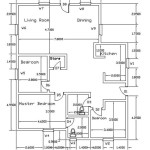
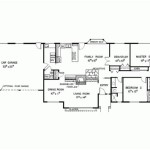
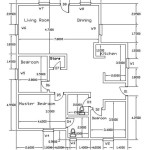
A floor plan is a scaled-down two-dimensional diagram that shows the layout of a single story of a building. It provides a bird's-eye view of the arrangement of rooms, walls, doors, windows, and other features like stairs and fireplaces. Floor plans are essential documents in building construction, serving as blueprints for the entire construction process. They are used by architects, builders, engineers, interior designers, and homeowners to visualize the space and plan its functionality.
Key Purposes of Floor Plans
Floor plans serve multiple crucial purposes in building construction:
Visualization and Planning: Floor plans allow stakeholders to visualize the space before construction begins. This helps in understanding the relationship between different rooms, their sizes, and the overall flow of the building. They provide a platform for making informed decisions about space allocation and layout optimization. This visualization can be particularly helpful for clients to understand the final product and request changes early in the design process.
Construction Guidance: Builders and contractors rely heavily on floor plans during the construction phase. They act as a roadmap, guiding the placement of walls, doors, windows, plumbing fixtures, and electrical systems. This clear visual representation ensures that the building is constructed according to the design specifications, reducing errors and potential rework.
Cost Estimation and Budgeting: Accurate floor plans are crucial for estimating construction costs. They enable accurate calculations of material quantities, labor requirements, and overall project timelines. This information is essential for developing a realistic budget and managing project finances effectively.
Key Components of a Floor Plan
A comprehensive floor plan includes various essential components:
Walls: Floor plans clearly depict the location and thickness of all walls, both exterior and interior. Different line weights or patterns may be used to distinguish between load-bearing and non-load-bearing walls. Accurate wall placement is critical for structural integrity and defining the boundaries of each room.
Doors and Windows: The location, size, and swing direction of doors and windows are indicated on the floor plan. Specific symbols represent different types of doors and windows, such as sliding doors, casement windows, or bay windows. Proper placement of openings is crucial for natural light, ventilation, and accessibility.
Fixtures and Appliances: Floor plans show the location of plumbing fixtures like sinks, toilets, showers, and bathtubs. They also indicate the placement of kitchen appliances like refrigerators, ovens, and dishwashers. This information is essential for coordinating plumbing and electrical installations.
Dimensions and Scale: Floor plans are drawn to scale, providing accurate measurements of rooms, walls, and other features. Dimensions are typically indicated using dimension lines and numerical values. This allows builders to accurately construct the building according to the design specifications.
Room Labels and Areas: Each room on the floor plan is typically labeled with its intended function, such as bedroom, living room, or kitchen. The area of each room may also be indicated, providing valuable information for space planning and cost estimation.
Types of Floor Plans
Different types of floor plans cater to specific needs during the building construction process:
2D Floor Plans: These are the most common type of floor plan, providing a flat, two-dimensional view of the layout. They are used for basic layout planning, visualizing space relationships, and communicating design intent.
3D Floor Plans: These plans offer a more realistic and immersive view of the space, adding height and depth to the 2D layout. They can be helpful for visualizing the overall aesthetics and spatial relationships of the finished building. Clients often find 3D floor plans easier to understand.
Reflected Ceiling Plans (RCPs): While not strictly floor plans, RCPs are closely related. They show the layout of the ceiling, including lighting fixtures, HVAC vents, and other ceiling-mounted elements. RCPs are essential for coordinating electrical and mechanical work.
Detailed Floor Plans: These specialized plans include detailed information about specific components, such as electrical wiring, plumbing layouts, and HVAC ductwork. They are used by contractors and subcontractors to ensure the correct installation of building systems.
Floor plans are dynamic documents that may evolve during the design and construction process. Changes and revisions are often necessary to accommodate client requests, site conditions, or unforeseen circumstances. Effective communication and collaboration among all stakeholders are essential for managing these changes and ensuring the successful completion of the building project. The use of Building Information Modeling (BIM) software increasingly facilitates these collaborative efforts by creating a centralized, dynamic model of the building, including the floor plan.

Floor Plan Wikipedia

How To Read A Floor Plan Hensley Custom Building Group

Building Plans

Design Your Own House Floor Plans Roomsketcher
Project 2 Floor Plan Scientific Diagram

Construction Drawings Building Plan And Planning Permissions

From Floor Plans To Structural Drawings Understanding Construction Made Easy

Design Your Own House Floor Plans Roomsketcher

Do Floor Plans For Building Construction By Bhunia Fiverr

Create Floor Plans
Related Posts