Simple Zimbabwe Rural House Plans With Pictures
Zimbabwe's rural landscape is dotted with homes that reflect a blend of traditional building practices and modern influences. These houses, often built with locally sourced materials and designed to suit the climate, showcase a resourceful and practical approach to housing. The demand for simple, affordable, and functional rural house plans is consistently high, driving the evolution of construction techniques and designs. Understanding the key considerations for building a rural home in Zimbabwe, along with exploring diverse architectural styles and practical floor plan options, is essential for successful implementation. This article explores these aspects, focusing on simplicity, affordability, and suitability for the Zimbabwean rural context, illustrated with imagery where applicable.
Key Considerations for Rural House Construction in Zimbabwe
Building a house in rural Zimbabwe involves careful planning, taking into account various factors that are unique to the setting. The suitability of the land, access to resources, and community involvement are crucial elements of the construction process. Furthermore, the climatic conditions and local building regulations significantly influence the design and choice of construction materials. Ignoring these critical considerations can lead to costly setbacks, compromised structural integrity, and potential conflict with local customs and authorities.
One of the first steps is conducting a thorough site assessment. This includes evaluating the soil composition, drainage patterns, and topography of the land. Understanding the soil type is vital for determining the appropriate foundation design. For instance, expansive clay soils require different foundation solutions compared to sandy or rocky soils. Poor drainage can lead to water accumulation around the foundation, potentially causing structural damage over time. Similarly, steep slopes may require terracing or other earthwork to create a stable building platform.
Access to resources is another paramount consideration. Rural areas may lack the infrastructure necessary for readily obtaining building materials. Transporting materials from distant urban centers can significantly increase construction costs. Therefore, utilizing locally available resources, such as clay for bricks, stones for foundations, and thatch for roofing, can be a cost-effective and sustainable approach. Sourcing these materials responsibly and sustainably is also important for minimizing environmental impact.
Community engagement is often essential for the smooth execution of a construction project in a rural setting. Consulting with local leaders and community members can help to gain support, understand local building practices, and avoid potential conflicts. Utilizing local labor can also contribute to the local economy and foster a sense of ownership and pride within the community. Furthermore, obtaining necessary permits and approvals from local authorities is crucial for complying with building regulations and avoiding legal issues.
Climate plays a significant role in determining the design and construction of a rural house. Zimbabwe experiences a subtropical climate with distinct wet and dry seasons. Houses should be designed to provide adequate ventilation to mitigate the effects of heat during the dry season and protect against rainfall during the wet season. Overhanging eaves, strategically placed windows, and well-insulated roofs are essential for maintaining a comfortable indoor environment. Orientation of the house to maximize natural light and minimize direct sunlight exposure can also contribute to energy efficiency.
Exploring Different Architectural Styles for Rural Homes
While affordability and functionality are primary concerns, there is room for incorporating different architectural styles into rural house designs, reflecting individual preferences and cultural influences. Traditional Zimbabwean architecture offers a rich source of inspiration, while modern approaches can enhance comfort and convenience. Combining elements from different styles can create unique and appealing homes that are both practical and aesthetically pleasing.
Traditional Zimbabwean architecture often features round huts with conical thatched roofs. These structures are typically built with readily available materials such as mud bricks (dagga) and poles. The circular shape provides structural stability and efficient use of space. Thatched roofs offer excellent insulation, keeping the house cool during the day and warm at night. While traditional huts may lack modern amenities, they can be adapted to incorporate features such as windows, improved ventilation, and screened openings to prevent insect intrusion. Maintaining the aesthetic appeal of traditional architecture while adding these modern comforts is a common design approach.
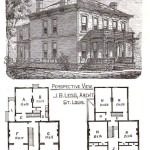
Another popular style involves rectangular houses built with burnt bricks and corrugated iron roofs. These houses are generally more durable and require less maintenance than traditional mud huts. The rectangular shape allows for easier division of space into separate rooms. Corrugated iron roofs are relatively inexpensive and easy to install, making them a popular choice in rural areas. However, they can be noisy during rainfall and may require insulation to reduce heat gain during hot weather. Brick houses often incorporate verandahs, providing shaded outdoor living spaces and protection from the elements.
Modern architectural styles are increasingly influencing rural house designs in Zimbabwe. These styles often emphasize simplicity, functionality, and sustainability. Features such as solar panels, rainwater harvesting systems, and energy-efficient lighting are becoming more common. Modern houses may incorporate open-plan living areas, large windows for natural light, and durable materials such as concrete and steel. Combining modern design elements with traditional construction techniques can create homes that are both comfortable and environmentally friendly.
The choice of architectural style ultimately depends on individual preferences, budget constraints, and the availability of materials and skilled labor. However, regardless of the chosen style, it is important to prioritize functionality, durability, and suitability for the local climate and environment. A well-designed house should provide a comfortable and safe living environment for its occupants while respecting the surrounding landscape and community.
Practical Floor Plan Options for Simple Rural Houses
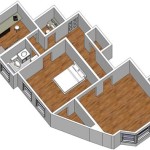
The floor plan of a rural house should be carefully designed to maximize usable space, provide adequate privacy, and facilitate everyday activities. Simple and efficient floor plans are often the most practical, especially for smaller houses. Consideration should be given to the number of occupants, their lifestyle, and their specific needs. Common elements of a rural house floor plan include a living area, sleeping quarters, a kitchen, and a bathroom or toilet. The arrangement of these spaces should promote ease of movement and efficient use of resources.
A typical floor plan for a small rural house may consist of a single main room that serves as a living and sleeping area, with a separate kitchen and a detached toilet. This layout is simple and cost-effective, but it may lack privacy and require careful organization to avoid clutter. Alternatively, the main room can be divided into separate living and sleeping areas using curtains, screens, or partition walls. This provides a degree of privacy without significantly increasing construction costs.
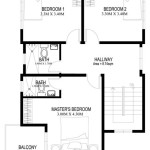
For larger houses, a more elaborate floor plan may include separate bedrooms, a living room, a dining area, a kitchen, and an indoor bathroom. The bedrooms should be located away from the living area to minimize noise and ensure privacy. The kitchen should be located near the dining area for convenient meal preparation and serving. An indoor bathroom provides greater comfort and hygiene compared to a detached toilet. The size and arrangement of these spaces should be tailored to the needs and preferences of the occupants.
The kitchen is often the heart of a rural home, and its design should be given careful consideration. A well-designed kitchen should provide adequate space for food preparation, cooking, and storage. A simple kitchen may consist of a countertop, a stove, and a sink. However, a more elaborate kitchen may include built-in cabinets, a refrigerator, and a separate food storage area. The choice of kitchen design depends on the available space, budget, and the cooking habits of the occupants.
Outdoor spaces, such as verandahs and courtyards, can also be integrated into the floor plan. Verandahs provide shaded outdoor living spaces and protect the house from the elements. Courtyards can create a sense of privacy and provide a safe space for children to play. These outdoor spaces can enhance the overall functionality and livability of the house. The incorporation of these features often depends on cultural norms, personal preferences, and budget availability.

Let S Build Our Rural Homes In Zimbabwe Ndokumbirawo Plan Iyi Anayo Kana Kuti Anoigona Uye I House Roof Design Affordable Plans Modern Bungalow

Smaller Neat And Simple Beautiful Well Built Modern House In The Rural Village Of Zimbabwe Ruralife Everyonehighlights

Rural House Plans S Zimbabwe Building Materials Suppliers

2 Roomed Cottage For Modern Rural Home Floor Plan Included

A Rural Home Design In Zimbabwe You Need To See

House Plan Design Tour 3 Bedroom Village Home To Be Built In Zimbabwe

2 Rooms House Design In Zimbabwe Rural Areas Tiktok

3 Bed Cottage House Plan Flat Roof Palmer Construction Zimbabwe

Beautiful Rural Homes In Zimbabwe You Must See 2024
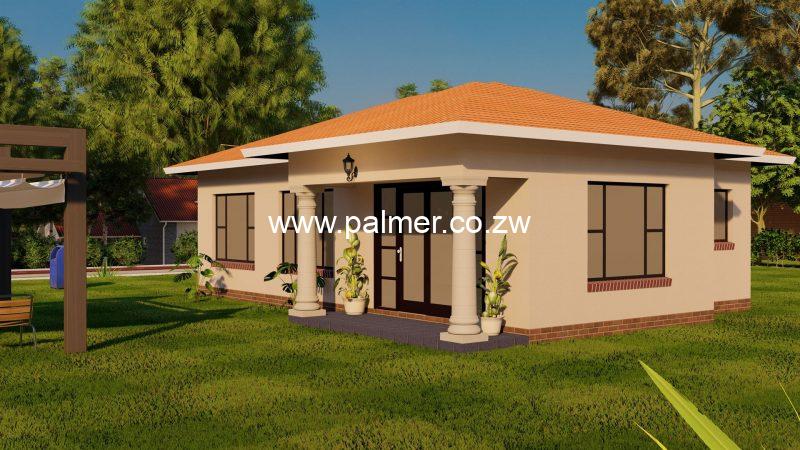

3 Bedroom High Density House Plan Palmer Construction Zimbabwe
Related Posts