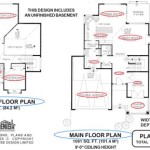
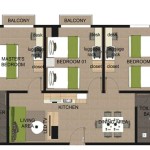
Understanding Simple 2D Plans with Dimensions
A simple 2D plan with dimensions is a fundamental tool in various fields, including architecture, engineering, interior design, and manufacturing. It serves as a visual representation of an object or space, providing precise measurements and spatial relationships necessary for accurate construction, design, or fabrication. Understanding how to interpret and create these plans is crucial for professionals and individuals involved in bringing ideas from concept to reality.
The core purpose of a 2D plan is to communicate geometric information clearly and concisely. Unlike 3D models which offer a more immersive and realistic view, 2D plans focus on providing orthogonal projections – views from directly above (plan view), from the side (elevation view), or from the front (section view). These projections, when combined with accurate dimensions, allow for precise understanding of sizes, shapes, and relative positions of different elements.
The simplicity of 2D plans lies in their ability to strip away unnecessary visual complexity and focus on the critical measurements. This makes them exceptionally useful for tasks like structural calculations, material estimations, and ensuring that different components fit together correctly. While modern technology offers sophisticated 3D modeling tools, 2D plans remain a standard due to their ease of creation, interpretation, and compatibility with various software platforms and traditional construction methods.
Key Elements of a 2D Plan
A well-constructed 2D plan incorporates several key elements that contribute to its clarity and accuracy. These elements include lines, dimensions, symbols, annotations, and a title block. Each component plays a specific role in conveying essential information about the object or space being represented.
Lines in a 2D plan represent edges, boundaries, and features. Different line types are used to distinguish between different types of elements. For instance, solid lines typically represent visible edges, while dashed lines indicate hidden edges or features. Centerlines are commonly used to denote the center of a circle or symmetrical object. The thickness of the lines can also be significant, with thicker lines often used to emphasize important features or boundaries.
Dimensions are arguably the most critical element of a 2D plan as they specify the exact size and location of each feature. Dimensions are typically displayed as numerical values accompanied by extension lines, dimension lines, and arrowheads. Extension lines extend from the feature being dimensioned, while the dimension line indicates the distance being measured. The arrowheads point to the extension lines, clearly indicating the endpoints of the measurement. The units of measurement (e.g., millimeters, inches, feet) should be clearly stated on the plan.
Symbols are used to represent specific objects or materials in a standardized way. Architectural plans, for example, use symbols to denote doors, windows, plumbing fixtures, and electrical outlets. Structural plans use symbols to represent beams, columns, and reinforcing steel. These symbols ensure consistency and clarity across different plans and projects. A legend or key is typically provided to explain the meaning of each symbol used in the plan.
Annotations are textual notes that provide additional information or clarification about specific features or aspects of the plan. Annotations can include material specifications, manufacturing instructions, or any other relevant details that cannot be easily conveyed through lines, dimensions, or symbols. Annotations should be concise, clear, and placed close to the feature they refer to.
The title block is a standardized area on the plan that contains important information about the project, such as the project name, drawing title, drawing number, revision number, date, and the name of the designer or architect. The title block serves as a record of the plan's history and provides essential context for its interpretation.
Importance of Accurate Dimensions
The accuracy of dimensions in a 2D plan is paramount to its usefulness. Inaccurate dimensions can lead to significant errors during construction, manufacturing, or any other activity based on the plan. These errors can result in wasted materials, delays, increased costs, and even structural failures.
To ensure accurate dimensions, it is essential to use precise measuring tools and techniques. In manual drafting, rulers, compasses, and protractors are used to measure and draw elements accurately. In computer-aided design (CAD) software, dimensions are automatically generated based on the geometric model. However, it is still crucial to verify the accuracy of these dimensions and to ensure that they are consistent with the design intent.
Dimensional tolerances should also be considered when specifying dimensions. A tolerance is the allowable variation in a dimension. Specifying appropriate tolerances is important to ensure that parts or components can be manufactured or assembled correctly. Tolerances are typically expressed as a plus or minus value (e.g., ±0.1 mm) or as a range (e.g., 10.0 mm - 10.2 mm).
Dimensioning conventions should be followed consistently to avoid ambiguity. These conventions dictate how dimensions are placed and displayed on the plan. For example, dimensions should generally be placed outside the object being dimensioned, and they should not cross any lines unnecessarily. The orientation of dimension text should be consistent and easy to read. Following these conventions helps to ensure that the dimensions are easily understood and interpreted correctly.
Regularly reviewing and verifying dimensions is crucial, especially when making changes to the plan. Even small changes can affect the accuracy of other dimensions, so it is important to update all dimensions that are affected by the changes. This helps to prevent errors and ensure that the plan remains accurate and reliable.
Applications of 2D Plans with Dimensions
2D plans with dimensions find applications across a wide range of industries and disciplines. Their versatility and simplicity make them an indispensable tool for visualizing, communicating, and executing designs.
In architecture, 2D plans are used to create floor plans, elevation views, and section views of buildings. These plans provide detailed information about the layout of rooms, the placement of doors and windows, and the overall structure of the building. Dimensions on these plans are crucial for accurately constructing the building according to the design specifications.
In engineering, 2D plans are used to design and manufacture mechanical components, electrical circuits, and structural systems. Mechanical engineers use 2D plans to create detailed drawings of machine parts, specifying their dimensions, tolerances, and material specifications. Electrical engineers use 2D plans to design circuit boards and wiring diagrams, indicating the placement of components and the routing of wires. Structural engineers use 2D plans to design bridges, buildings, and other structures, specifying the size and location of beams, columns, and other structural elements.
Interior designers use 2D plans to create layouts of rooms, specifying the placement of furniture, fixtures, and other decorative elements. Dimensions on these plans are crucial for ensuring that the furniture and fixtures fit properly in the space and that the overall design is aesthetically pleasing and functional.
Manufacturing industries rely heavily on 2D plans to guide the fabrication of products. From simple consumer goods to complex machinery, 2D plans provide the necessary dimensional information for cutting, shaping, and assembling parts. These plans are often used in conjunction with computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) systems to automate the manufacturing process.
In landscaping, 2D plans are used to design gardens, parks, and other outdoor spaces. These plans specify the placement of plants, trees, walkways, and other features, and they include dimensions for measuring distances and areas. Landscaping plans are used to create aesthetically pleasing and functional outdoor environments.
The ability to create and interpret simple 2D plans with dimensions is a valuable skill that can be applied in many different contexts. Whether designing a building, manufacturing a product, or planning a garden, 2D plans provide a clear and concise way to communicate design information and ensure that projects are executed accurately.

Create Professional 2d Floor Plans Roomsketcher

2d Floor Plans Plan Design Home Small Kitchen

Create Professional 2d Floor Plans Roomsketcher

12 Examples Of Floor Plans With Dimensions

2d Floor Plan Commercial Real Estate It All

Beautiful 2d Floor Plan Ideas Engineering Discoveries Home Map Design Building House Plans Designs

2d Floor Plan Archives Page 2 Of 6 Dk Home Designx

Beautiful 2d Floor Plan Ideas Engineering Discoveries Square House Plans Bungalow Simple

2d Drawing Gallery Floor Plans House

Floor Plans With Dimensions Including Examples Cedreo
Related Posts