Most Economical House Plan: Balancing Cost and Comfort
The pursuit of homeownership often involves a careful consideration of budget. Selecting an economical house plan is paramount for those seeking to minimize construction costs without sacrificing essential living spaces and functionality. An economical house plan prioritizes efficient use of materials, simplified construction processes, and reduced energy consumption, ultimately leading to lower initial investment and long-term operational expenses.
Designing a house for affordability requires a strategic approach encompassing various factors, starting from the initial design phase to material selection and construction techniques. The most economical house plans are not necessarily the smallest, but rather those that maximize value for every square foot. This involves making informed decisions about the layout, materials, and features to achieve a balance between cost savings and desired living standards.
Key Considerations for Economical House Plans
Numerous factors influence the overall cost of building a house. Understanding these key elements is crucial for selecting a plan that fits within a specific budget. Neglecting these considerations can lead to unexpected expenses and compromise the project's economic viability.
Simplicity of Design: Complex architectural features, intricate rooflines, and non-standard shapes significantly increase construction costs. A simple, rectangular or square floor plan is inherently more economical to build. These shapes minimize the need for specialized materials and labor, simplifying the framing and roofing processes. Avoiding unnecessary curves, angles, and embellishments can result in substantial savings. Simpler designs also facilitate easier maintenance and long-term repairs.
Complicated rooflines, with multiple gables, dormers, and valleys, require more materials and skilled labor for installation. A simpler roof design, such as a gable or hip roof with a moderate pitch, is easier and less expensive to construct. The choice of roofing material also plays a significant role. Asphalt shingles are generally more affordable than tile, slate, or metal roofing. However, the longevity and energy efficiency of different materials should be considered to evaluate their long-term cost-effectiveness.
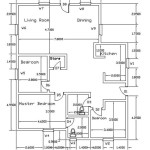
Optimizing the use of space is another critical factor. Open floor plans, while often desirable for their aesthetic appeal and social connectivity, can sometimes be more expensive due to the need for longer spans and stronger structural support. Carefully consider the balance between open spaces and enclosed rooms to maximize usable area while minimizing structural costs. Multifunctional spaces, such as a living room that doubles as a home office, can also reduce the overall square footage required, thereby lowering construction costs.
Size and Layout Efficiency: The size of the house directly impacts the cost of materials and labor. Building a smaller house is generally more economical, but it's essential to ensure that the layout is functional and meets the needs of the occupants. A well-designed smaller space can feel larger and more comfortable than a poorly designed larger space. The layout should minimize wasted space, such as long hallways or unused corners. Consider incorporating built-in storage solutions to maximize space utilization.
The location of rooms within the house can also affect construction costs. Grouping bathrooms and kitchens together, for example, can reduce plumbing costs by centralizing water lines. Similarly, locating the laundry room near the bedrooms can simplify the installation of plumbing and electrical connections. Carefully planning the layout to optimize efficiency and minimize the runs of utilities can lead to significant cost savings.
Vertical stacking of plumbing fixtures, such as placing a bathroom above the kitchen, can further reduce plumbing costs. This simplifies the drainage system and minimizes the amount of piping required. However, it's important to ensure that the floor plan allows for this stacking without compromising the overall functionality or aesthetic appeal of the house.
Material Selection and Construction Methods: The choice of building materials significantly influences the overall cost of construction. Opting for locally sourced materials can reduce transportation costs and support local businesses. Standard-sized materials, such as lumber and drywall, are typically more affordable than custom-sized materials. Using readily available materials also simplifies the construction process and reduces the likelihood of delays due to supply chain issues.
Prefabricated components, such as trusses and wall panels, can speed up the construction process and reduce labor costs. These components are manufactured off-site in a controlled environment, ensuring consistent quality and reducing waste. Using prefabricated elements can also minimize the amount of time required for on-site construction, which can translate to lower labor costs and faster project completion.
Consider the long-term durability and maintenance requirements of different materials. While some materials may have a lower initial cost, they may require more frequent repairs or replacements, leading to higher overall costs in the long run. Investing in durable, low-maintenance materials can save money over the lifespan of the house. Carefully evaluate the life-cycle cost of different materials before making a decision.
Strategies for Reducing Building Costs
Beyond the basic design considerations, several strategies can be implemented to further reduce the cost of building a house. These strategies often involve making smart choices about features, finishes, and construction practices.
Energy-Efficient Design: Incorporating energy-efficient features into the house plan can significantly reduce long-term operating costs. Proper insulation, energy-efficient windows, and a high-efficiency HVAC system can lower heating and cooling bills. While these features may have a higher initial cost, they will pay for themselves over time through reduced energy consumption. Consider solar panels or other renewable energy sources to further reduce reliance on traditional energy sources.
Proper insulation is crucial for maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature and reducing energy waste. Insulating walls, ceilings, and floors can prevent heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer. The level of insulation required will vary depending on the climate. Consult with a building professional to determine the appropriate insulation levels for the specific location.
Energy-efficient windows and doors can also significantly reduce energy loss. Look for windows and doors with low U-values and high solar heat gain coefficients (SHGC) for optimal energy performance. Consider double-paned or triple-paned windows with low-E coatings to further reduce heat transfer. Sealing air leaks around windows and doors can also prevent drafts and reduce energy waste.
DIY and Owner-Builder Options: Depending on one's skills and experience, performing some of the construction tasks oneself can save money on labor costs. Tasks such as painting, landscaping, and installing flooring can often be done by the homeowner, provided they have the necessary skills and time. However, it's important to be realistic about one's abilities and avoid taking on tasks that are beyond one's expertise. Improperly executed work can lead to costly repairs and delays.
Acting as the owner-builder, meaning taking on the responsibility of managing the construction project, can also save money by eliminating the need for a general contractor. However, this option requires significant time, organizational skills, and knowledge of the building process. The owner-builder is responsible for hiring subcontractors, obtaining permits, and ensuring that the project is completed on time and within budget.
Before taking on any DIY or owner-builder tasks, it's important to research local building codes and regulations. Obtain the necessary permits and ensure that all work is performed in compliance with these regulations. Even if performing the work oneself, it's often advisable to consult with a qualified professional for guidance and advice.
Value Engineering and Cost-Cutting Measures: Value engineering involves systematically analyzing the design and construction process to identify opportunities for cost savings without compromising the functionality or quality of the house. This may involve substituting materials, simplifying details, or streamlining construction methods.
One example of value engineering is to use standard-sized windows and doors instead of custom-sized ones. Standard-sized windows and doors are typically more affordable and readily available. Similarly, using standard lumber sizes can reduce waste and simplify the framing process.
Another cost-cutting measure is to minimize the number of custom features and finishes. Simple, streamlined designs are generally more affordable to build than elaborate, ornate designs. Choosing standard finishes, such as paint colors and flooring materials, can also save money. Consider focusing on high-impact areas, such as the kitchen and bathrooms, and opting for more economical finishes in other areas of the house.
Long-Term Cost Savings Considerations
An economical house plan not only focuses on reducing initial construction costs but also aims to minimize long-term operating expenses. This includes considering factors such as energy efficiency, water conservation, and maintenance requirements.
Water Conservation Features: Installing water-efficient fixtures, such as low-flow toilets, showerheads, and faucets, can significantly reduce water consumption and lower water bills. Consider installing a rainwater harvesting system to collect rainwater for irrigation and other non-potable uses. Landscaping with drought-resistant plants can also reduce water consumption and minimize the need for irrigation.
A well-designed irrigation system can also conserve water by delivering water directly to the roots of plants, minimizing water loss due to evaporation. Consider using drip irrigation or soaker hoses for efficient watering. Mulching around plants can also help to retain moisture in the soil and reduce the need for frequent watering.
Low-Maintenance Materials: Choosing materials that require minimal maintenance can save time and money in the long run. For example, vinyl siding is generally more low-maintenance than wood siding, as it does not require painting or staining. Similarly, concrete pavers are typically more durable and low-maintenance than asphalt pavement.
When selecting materials, consider their resistance to pests, rot, and other forms of deterioration. Investing in durable, long-lasting materials can reduce the need for repairs and replacements, saving money over the lifespan of the house. Choosing materials that are easy to clean and maintain can also save time and effort.
Future Expansion Possibilities: While building a smaller house may be more economical in the short term, consider the potential need for future expansion. Designing the house with the possibility of adding an addition or finishing an unfinished basement can provide flexibility and avoid the need to build a larger house initially.
Planning for future expansion can involve adding stub-outs for plumbing and electrical connections in anticipation of future renovations. Also, properly orienting the house on the lot can maximize the available space for future additions. Consult with a building professional to discuss options for future expansion and to ensure that the design is compatible with the intended renovations.

Affordable House Plans Our Est To Build Blog Homeplans Com
Est House Plans To Build Simple With Style Blog Eplans Com

Affordable Home Design Efficient Floor Plans

Est House Plans To Build Simple With Style Blog Eplans Com

Building On The Affordable House Plans Of 2024 Houseplans Blog Com

Est House Plans To Build Simple With Style Blog Eplans Com

Est House Plans To Build Simple With Style Blog Eplans Com

Stylish And Simple Inexpensive House Plans To Build Houseplans Blog Com

Modern Style House Plan 3 Beds 2 Baths 2115 Sq Ft 497 31 Cabin Plans Small

Efficient Use Of Space Multiple Versions 5146mm Architectural Designs House Plans
Related Posts