How To Make A Floor Plan In Blender
Blender, a powerful and versatile 3D creation suite, offers robust tools for architectural visualization, including creating accurate and detailed floor plans. This guide will outline the process of generating a 2D floor plan from a 3D model within Blender, leveraging its modeling and rendering capabilities.
The first step involves setting up the Blender environment. Users should ensure they are working in the appropriate workspace, typically the "Layout" workspace which offers a comprehensive view of various editors. This workspace allows for easy navigation between 3D views, image editors, and other essential panels.
Importing existing architectural models, if available, is the next logical step. Blender supports various file formats, including .obj, .fbx, and .dae. Selecting "File" then "Import" from the top menu bar will present the available formats. Once imported, the model will appear within the 3D viewport, ready for manipulation.
If starting from scratch, Blender's modeling tools will be employed to construct the 3D model of the building's interior. Commonly used tools include the "Extrude" tool for creating walls from 2D shapes, the "Loop Cut" tool for adding detail, and various mesh editing options. The precision of the 3D model directly impacts the accuracy of the final floor plan.
After the 3D model is complete or imported, setting up the camera for an orthographic top-down view is crucial. Select the camera object in the scene. In the "Object Data Properties" panel (the camera icon), change the camera type from "Perspective" to "Orthographic." This eliminates perspective distortion, essential for an accurate floor plan. Position the camera directly above the model using the translate and rotate tools (G and R keys, respectively) to achieve a bird's-eye view. Adjust the "Orthographic Scale" property to encompass the entire model within the camera frame.
Rendering the top-down view is the next step. Within the "Output Properties" tab (the printer icon), specify the desired resolution and output file format (e.g., PNG, JPEG). Ensure the "Render Engine" is set to "Cycles" or "Eevee" depending on the complexity of the model and desired rendering quality. Click the "Render Image" button to initiate the rendering process. The resulting image will represent a raw, unrefined floor plan.
Post-processing the rendered image is vital for clarity and presentation. This can be achieved within Blender's compositor or using external image editing software. Cropping the image to remove excess blank space and adjusting contrast and brightness levels can significantly enhance readability. Adding labels for rooms and dimensions using annotation tools will further improve the floor plan's utility.
Utilizing Freestyle, Blender's non-photorealistic rendering engine, can generate line art style floor plans. Enable Freestyle in the "Render Properties" tab. Adjusting Freestyle settings, such as line thickness and color, provides control over the final output's appearance. This method generates clean, vector-like lines ideal for schematic representations.
Alternatively, users can leverage Blender's "Freestyle SVG Exporter" addon. This addon exports the Freestyle lines as Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) files, suitable for editing in vector graphics software like Inkscape or Adobe Illustrator. SVG format allows for easy manipulation and scaling of the floor plan elements without loss of quality.
For more complex projects, consider utilizing Blender's layer management system to organize different elements of the floor plan, such as walls, furniture, and fixtures. Each element can be assigned to a specific layer for easier visibility control and selective rendering.
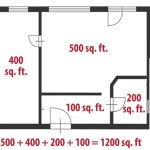
Adding dimensions to the floor plan enhances its practical value. While Blender doesn't have a built-in dimensioning tool specifically for floor plans, several addons can provide this functionality. Alternatively, dimensions can be added during the post-processing phase using image editing software.
Material and texture considerations are important, particularly if generating more visually rich floor plans. Applying different materials and textures to the 3D model (e.g., wood for flooring, tile for bathrooms) can visually distinguish different areas within the floor plan. These material differences will be reflected in the rendered image.
Finally, exporting the finished floor plan in a suitable format is the last step. Common formats include PNG, JPEG for raster images, and SVG, PDF for vector-based output. Selecting the appropriate format depends on the intended use of the floor plan.

Blender For Noobs 10 How To Create A Simple Floorplan In

How To Make 3d Floor Plan In Blender Beginners Guide Part 1

Sketching A Floor Plan In Blender 3d Architect

How To Make 3d Floor Plan In Blender Best Method Modeling

Quickest Floor Plan Model In Blender Part 1

Sketching A Floor Plan In Blender 3d Architect

How To Make 3d Floor Plan In Blender

How To Make 3d Floor Plan In Blender Best Method Modeling

How To Create A 3d Floor Plan In Blender 3 0

Create A 3d Floor Plan Model From An Architectural Schematic In Blender Blendernation
Related Posts